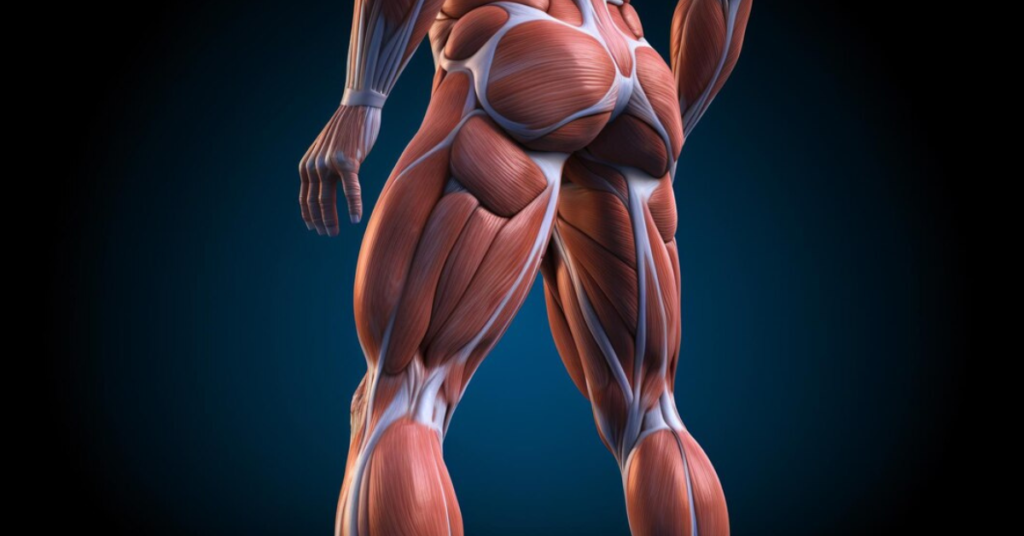
The gluteal muscles, often referred to as the glútem, are a group of three muscles located in the buttocks. These muscles include the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. They are vital for various movements and functions of the lower body, such as walking, running, jumping, and maintaining stability in different postures. This article explores the anatomy, function, and significance of the gluteal muscles, highlighting their importance for overall physical health and performance.
Anatomy of the Glútem
Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus is the largest and most superficial of the three gluteal muscles. It originates from the dorsal ilium, sacrum, and coccyx and inserts into the iliotibial tract and the gluteal tuberosity of the femur. The gluteus maximus is primarily responsible for the extension, outward rotation, and abduction of the hip joint. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining the erect posture and assisting in movements that require forceful hip extension, such as rising from a sitting position, climbing stairs, and running.
Gluteus Medius
The gluteus medius is situated beneath the gluteus maximus and lies more towards the lateral side of the hip. It originates from the outer surface of the ilium and inserts into the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur. The gluteus medius is primarily responsible for the abduction and medial rotation of the hip. It also plays a significant role in stabilizing the pelvis during walking, preventing the opposite side of the pelvis from dropping.
Gluteus Minimus
The gluteus minimus is the smallest and deepest of the gluteal muscles. It originates from the outer surface of the ilium, just below the gluteus medius, and inserts into the anterior aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur. The gluteus minimus works in concert with the gluteus medius to abduct and medially rotate the hip. It also contributes to pelvic stability during gait.
Function of the Glútem
Movement and Locomotion
The gluteal muscles are essential for a wide range of movements and activities. They play a critical role in hip extension, abduction, and rotation, which are necessary for walking, running, jumping, and other forms of locomotion. The gluteus maximus, in particular, provides the powerful hip extension required for movements like sprinting and climbing.
Postural Stability
The gluteal muscles contribute significantly to postural stability. The gluteus medius and minimus, in particular, stabilize the pelvis and prevent excessive tilting during activities such as walking and standing on one leg. This stabilization is crucial for maintaining balance and proper alignment of the lower body.
Force Generation
The gluteus maximus is one of the strongest muscles in the human body and is capable of generating significant force. This force generation is essential for explosive movements, such as jumping, sprinting, and heavy lifting. The strength of the gluteal muscles is a key factor in athletic performance and overall functional capacity.
Injury Prevention
Strong and well-functioning gluteal muscles can help prevent injuries in the lower back, hips, and knees. The gluteal muscles provide support and stability to these areas, reducing the risk of strains, sprains, and other injuries. Weakness or dysfunction in the gluteal muscles can lead to compensatory movements and increased stress on other parts of the body, potentially resulting in injury.
Importance of the Glútem in Physical Health and Performance
Enhancing Athletic Performance
For athletes, the gluteal muscles are crucial for performance in various sports and physical activities. The strength and power of the gluteus maximus contribute to speed and agility, while the stability provided by the gluteus medius and minimus supports efficient and effective movement patterns. Training the gluteal muscles can lead to improved athletic performance and reduced risk of injury.
Improving Posture and Reducing Pain
The gluteal muscles play a significant role in maintaining proper posture and alignment of the pelvis and lower back. Strengthening these muscles can help alleviate lower back pain and improve overall posture. Poor posture and weak gluteal muscles are often linked to chronic pain and discomfort in the lower back and hips.
Supporting Functional Movement
The gluteal muscles are essential for functional movements and daily activities. Tasks such as rising from a chair, climbing stairs, and carrying heavy objects all require the activation of the gluteal muscles. Strengthening these muscles can enhance the ability to perform everyday tasks with ease and efficiency.
Promoting Overall Physical Health
Strong gluteal muscles contribute to overall physical health and well-being. They support the spine and pelvis, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues and promoting better mobility and flexibility. Regular exercise and targeted training of the gluteal muscles can lead to improved physical fitness and a higher quality of life.
Training and Strengthening the Glútem
Resistance Exercises
Resistance training is one of the most effective ways to strengthen the gluteal muscles. Exercises such as squats, deadlifts, lunges, and hip thrusts specifically target the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus. Incorporating these exercises into a regular workout routine can help build strength and endurance in the gluteal muscles.
Bodyweight Exercises
Bodyweight exercises are also beneficial for training the gluteal muscles. Movements such as glute bridges, step-ups, and single-leg squats can be performed without any equipment and are effective for activating and strengthening the gluteal muscles. These exercises can be easily modified to increase intensity and challenge the muscles further.
Flexibility and Mobility
Maintaining flexibility and mobility in the gluteal muscles is important for overall function and performance. Stretching exercises, such as pigeon pose, seated forward bend, and hip flexor stretches, can help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. Incorporating regular stretching and mobility work into a fitness routine can enhance the function and health of the gluteal muscles.
Activation Techniques
Gluteal muscle activation exercises are designed to engage and activate the gluteal muscles before more intense workouts. These exercises, such as clamshells, band walks, and fire hydrants, help to “wake up” the gluteal muscles and ensure they are properly engaged during subsequent exercises. Activation techniques are particularly useful for individuals with weak or inactive gluteal muscles.
Common Issues and Injuries
Gluteal Tendinopathy
Gluteal tendinopathy is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the tendons of the gluteal muscles. It is often caused by overuse, repetitive strain, or improper biomechanics. Treatment typically involves rest, physical therapy, and targeted exercises to strengthen and rehabilitate the affected muscles and tendons.
Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis syndrome occurs when the piriformis muscle, located near the gluteal muscles, compresses the sciatic nerve. This compression can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the buttocks and down the leg. Stretching and strengthening exercises, along with physical therapy, can help alleviate symptoms and address the underlying muscle imbalances.
Gluteal Strain
A gluteal strain is a tear or overstretching of the gluteal muscles. It can occur due to sudden movements, excessive force, or improper warm-up before exercise. Treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), followed by gradual rehabilitation and strengthening exercises to prevent re-injury.
Hip Bursitis
Hip bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint. It can cause pain and discomfort in the hip and buttocks area. Treatment typically involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve joint stability.
Conclusion
The gluteal muscles, or glútem, are essential for various movements and functions of the lower body. Understanding the anatomy, function, and significance of these muscles is crucial for overall physical health and performance. By incorporating targeted exercises, maintaining flexibility and mobility, and addressing any issues or injuries promptly, individuals can optimize the function and strength of their gluteal muscles. Whether for athletic performance, injury prevention, or daily functional activities, the glútem muscles play a vital role in supporting a healthy and active lifestyle.